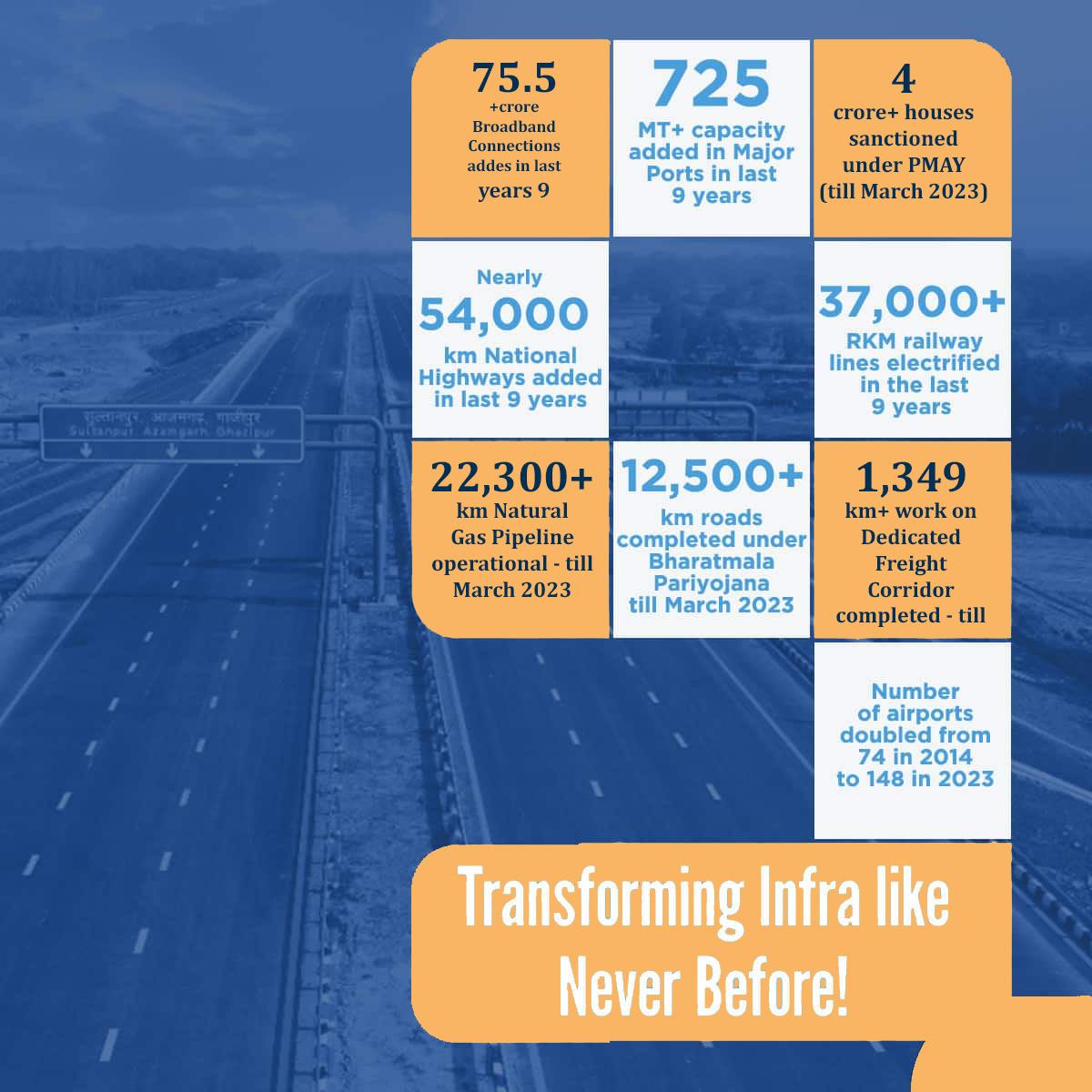
India witnessed fast-paced infrastructure development in all sectors in the last nine years
The Government has made unprecedented investments in modern infrastructure in the last nine years taking the country to new heights. The quality of a country’s infrastructure is a key determinant in shaping its economic trajectory. The Narendra Modi-led Govt has kept infrastructure at the front and centre of its development agenda.
PM Modi specifically drew attention to the fact that these efforts are forging an infrastructure landscape that is unmatched in its excellence.Additionally, the Prime Minister highlighted that each sector has experienced rapid progress, creating a favourable environment for the emergence of a developed India.
We nurtured the roots of growth and development in India, shaping an infrastructure landscape that is unparalleled. Every sector has witnessed swift advancement, setting the stage for a developed India
The Gati Shakti Master Plan, introduced by PM Modi on 13 October 2021, stands as a significant undertaking that aims to enhance collaboration among various ministries, states, and departments.
Acknowledging the pivotal role of port infrastructure in driving economic growth, the Modi government has undertaken ambitious endeavours to enhance and modernise India's ports.
Under the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan For Connectivity, the Indian Government has introduced a novel digital tool aimed at addressing the challenges of project delays
Over the past years, the government has successfully launched 15 Vande Bharat trains, with plans to manufacture an additional 400 Vande Bharat express trains in the next three years
In a significant move, the government demonstrated its boldness in the budget by raising the capital investment outlay to Rs 7.5 lakh crores.
PM Gati Shakti: A Game Changer

PM Gati Shakti: A Game Changer in India’s Infrastructure Landscape
Transforming Transportation and Infrastructure
Prime Minister Gati Shakti is a monumental initiative introduced by the Government of India, designed to revolutionize the country’s infrastructure and transportation networks. This visionary project, with its integration of various modes of transportation and cutting-edge technology, has the potential to be a game-changer for India.
Seamless Connectivity
One of the primary goals of PM Gati Shakti is to create a seamless and efficient logistics ecosystem by integrating roads, railways, ports, airports, and waterways. This integration will eliminate bottlenecks and inefficiencies that have historically hampered the flow of goods and people within the country.
Economic Growth and Job Creation
The project’s core objective is to accelerate economic growth and create jobs. By streamlining transportation and infrastructure networks, PM Gati Shakti will significantly reduce transportation costs, boost trade, and enhance connectivity between urban and rural areas. This, in turn, will stimulate economic activity, particularly in industries reliant on efficient logistics, and create millions of jobs.
Digital Transformation
PM Gati Shakti is not just about physical infrastructure; it’s also a digital transformation initiative. By leveraging technologies like GIS mapping and real-time tracking, it will enhance the efficiency of transportation and logistics operations. This technological integration will lead to better route planning, reduced delays, and improved resource allocation.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
The project places a strong emphasis on sustainability and environmental consciousness. It promotes the development of green and energy-efficient infrastructure, aligning with India’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions and conserving the environment. By investing in eco-friendly solutions, PM Gati Shakti showcases a forward-looking approach to infrastructure development.
Enhancing Global Competitiveness
PM Gati Shakti is not only about domestic development but also about enhancing India’s global competitiveness. By reducing transportation time and costs for businesses, it will make Indian industries more competitive on the international stage. This improved connectivity will facilitate the movement of goods and people across the country, enabling businesses to reach wider markets.
Ease of Doing Business and Foreign Investment
In addition to improving connectivity, PM Gati Shakti will simplify regulatory processes, reducing bureaucratic hurdles for businesses. This will enhance the ease of doing business in India, attracting more foreign investment and fostering innovation. A business-friendly environment will be crucial in India’s journey to become a global economic powerhouse.
Inclusive Development
PM Gati Shakti’s comprehensive approach also seeks to bridge the rural-urban divide. By improving connectivity in rural areas, it will unlock the economic potential of regions that were previously underserved. This inclusive development strategy aims to ensure that the benefits of economic growth reach every corner of the country.
In conclusion, PM Gati Shakti is poised to be a game-changer in India’s infrastructure landscape. It has the potential to modernize transportation and infrastructure networks, stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and enhance the quality of life for millions of Indians. As India continues on its development journey, PM Gati Shakti stands out as a visionary initiative that holds the power to transform the nation’s infrastructure and drive its progress in the 21st century.
Port Infrastructure

Port Infrastructure: The Backbone of Global Trade
Introduction
Port infrastructure plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade and commerce. Ports are not just gateways for goods; they are economic engines, connecting nations, and driving economic growth. In this article, we explore the significance of port infrastructure and its multifaceted impact on global trade and regional development.
Key Components of Port Infrastructure
Port infrastructure encompasses a range of elements:
Terminals and Berths: These are the physical areas where ships load and unload cargo. The efficiency of these terminals is critical for reducing turnaround times.
Navigation Channels: Dredged and maintained channels allow vessels to access ports safely, even with large drafts.
Cargo Handling Equipment: Cranes, forklifts, and conveyor systems are essential for efficient cargo handling.
Storage Facilities: Warehouses and yards are crucial for temporary storage of cargo.
Connectivity: Ports need well-developed road and rail links to ensure seamless transportation of goods to and from the hinterland.
Global Trade Facilitation
Ports are gateways to the global economy. They serve as interfaces between ships and land-based transportation networks. Efficient port infrastructure reduces the time it takes for goods to reach their destination, lowering transportation costs, and making products more competitive in the global market. This, in turn, promotes international trade and economic growth.
Job Creation and Economic Impact
Port infrastructure creates direct and indirect employment opportunities. Jobs are generated not only within the port itself but also in industries related to shipping and logistics. The economic impact of ports extends to the entire region, attracting businesses and stimulating local economies.
Regional Development
Ports often become catalysts for regional development. The development of port-related industries and the improvement of transportation networks around ports can transform underdeveloped areas into thriving economic centers. The “Port-led Industrialization” strategy, as seen in India’s Sagarmala program, exemplifies this concept.
Environmental Concerns and Sustainability
Modern port infrastructure focuses on sustainability. Ports are adopting cleaner technologies to reduce environmental impacts, such as lowering emissions and minimizing habitat disruption. They also invest in better waste management and energy-efficient operations.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite their importance, ports face several challenges. Infrastructure maintenance and expansion are costly endeavors. Environmental concerns and regulatory compliance add complexity. Future trends in port infrastructure include automation and digitization, which can enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
Conclusion
Port infrastructure is the lifeblood of international trade, connecting economies and fostering global prosperity. Its impact reaches far beyond the docks, influencing regional development and job creation. To remain competitive in the rapidly changing global economy, nations must continue to invest in and upgrade their port infrastructure, balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability. Port infrastructure is not just about the movement of goods; it’s about shaping the future of nations and the world economy.
Improvement in connectivity

Introduction
Port infrastructure plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade and commerce. Ports are not just gateways for goods; they are economic engines, connecting nations, and driving economic growth. In this article, we explore the significance of port infrastructure and its multifaceted impact on global trade and regional development.
Key Components of Port Infrastructure
Port infrastructure encompasses a range of elements:
Terminals and Berths: These are the physical areas where ships load and unload cargo. The efficiency of these terminals is critical for reducing turnaround times.
Navigation Channels: Dredged and maintained channels allow vessels to access ports safely, even with large drafts.
Cargo Handling Equipment: Cranes, forklifts, and conveyor systems are essential for efficient cargo handling.
Storage Facilities: Warehouses and yards are crucial for temporary storage of cargo.
Connectivity: Ports need well-developed road and rail links to ensure seamless transportation of goods to and from the hinterland.
Global Trade Facilitation
Ports are gateways to the global economy. They serve as interfaces between ships and land-based transportation networks. Efficient port infrastructure reduces the time it takes for goods to reach their destination, lowering transportation costs, and making products more competitive in the global market. This, in turn, promotes international trade and economic growth.
Job Creation and Economic Impact
Port infrastructure creates direct and indirect employment opportunities. Jobs are generated not only within the port itself but also in industries related to shipping and logistics. The economic impact of ports extends to the entire region, attracting businesses and stimulating local economies.
Regional Development
Ports often become catalysts for regional development. The development of port-related industries and the improvement of transportation networks around ports can transform underdeveloped areas into thriving economic centers. The “Port-led Industrialization” strategy, as seen in India’s Sagarmala program, exemplifies this concept.
Environmental Concerns and Sustainability
Modern port infrastructure focuses on sustainability. Ports are adopting cleaner technologies to reduce environmental impacts, such as lowering emissions and minimizing habitat disruption. They also invest in better waste management and energy-efficient operations.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite their importance, ports face several challenges. Infrastructure maintenance and expansion are costly endeavors. Environmental concerns and regulatory compliance add complexity. Future trends in port infrastructure include automation and digitization, which can enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
Conclusion
Port infrastructure is the lifeblood of international trade, connecting economies and fostering global prosperity. Its impact reaches far beyond the docks, influencing regional development and job creation. To remain competitive in the rapidly changing global economy, nations must continue to invest in and upgrade their port infrastructure, balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability. Port infrastructure is not just about the movement of goods; it’s about shaping the future of nations and the world economy.
Infrastructure as nation’s growth engine: Budget 2023

Introduction
Port infrastructure plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade and commerce. Ports are not just gateways for goods; they are economic engines, connecting nations, and driving economic growth. In this article, we explore the significance of port infrastructure and its multifaceted impact on global trade and regional development.
Key Components of Port Infrastructure
Port infrastructure encompasses a range of elements:
Terminals and Berths: These are the physical areas where ships load and unload cargo. The efficiency of these terminals is critical for reducing turnaround times.
Navigation Channels: Dredged and maintained channels allow vessels to access ports safely, even with large drafts.
Cargo Handling Equipment: Cranes, forklifts, and conveyor systems are essential for efficient cargo handling.
Storage Facilities: Warehouses and yards are crucial for temporary storage of cargo.
Connectivity: Ports need well-developed road and rail links to ensure seamless transportation of goods to and from the hinterland.
Global Trade Facilitation
Ports are gateways to the global economy. They serve as interfaces between ships and land-based transportation networks. Efficient port infrastructure reduces the time it takes for goods to reach their destination, lowering transportation costs, and making products more competitive in the global market. This, in turn, promotes international trade and economic growth.
Job Creation and Economic Impact
Port infrastructure creates direct and indirect employment opportunities. Jobs are generated not only within the port itself but also in industries related to shipping and logistics. The economic impact of ports extends to the entire region, attracting businesses and stimulating local economies.
Regional Development
Ports often become catalysts for regional development. The development of port-related industries and the improvement of transportation networks around ports can transform underdeveloped areas into thriving economic centers. The “Port-led Industrialization” strategy, as seen in India’s Sagarmala program, exemplifies this concept.
Environmental Concerns and Sustainability
Modern port infrastructure focuses on sustainability. Ports are adopting cleaner technologies to reduce environmental impacts, such as lowering emissions and minimizing habitat disruption. They also invest in better waste management and energy-efficient operations.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite their importance, ports face several challenges. Infrastructure maintenance and expansion are costly endeavors. Environmental concerns and regulatory compliance add complexity. Future trends in port infrastructure include automation and digitization, which can enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
Conclusion
Port infrastructure is the lifeblood of international trade, connecting economies and fostering global prosperity. Its impact reaches far beyond the docks, influencing regional development and job creation. To remain competitive in the rapidly changing global economy, nations must continue to invest in and upgrade their port infrastructure, balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability. Port infrastructure is not just about the movement of goods; it’s about shaping the future of nations and the world economy.